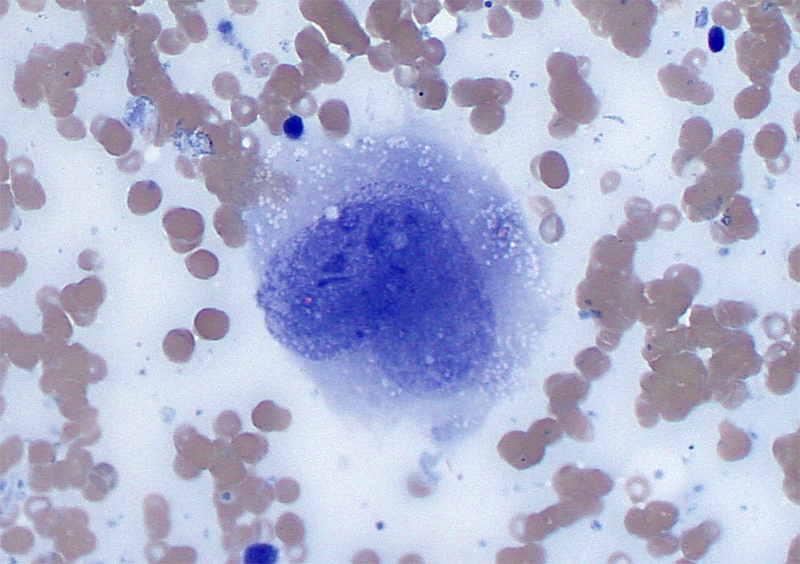
DOG, 7 y, male, histiocytic sarcoma
mod. Romanowsky, 100x oil
CELLS (General criteria)
Anisocytosis = difference in cell size
Polymorphism = difference in cell morphology
Decreased cell-to-cell adhesion (epithelial cells)
Changes in the degree of cellular differentiation
NUCLEUS
Shape
Polymorphism?
Irregular?
Size
Macrokaryosis?
Anisokaryosis?
Number
Multinucleation?
Odd numbers of nucelii?
Intracellular anisokaryosis?
Micronuclei?
Prominent?
Size:
> 2/3 size of a RBC?
Variable size within same nucleus?
Shape – irregular?
Number - >5?
MITOTIC FIGURES
Number – (in 5 high power fields or 10 low power 40 x magnification fields)
Abnormal ?
NUCLEAR TO CYTOPLASMIC RATIO
Increased?
Variable?
CYTOPLASM
Amount?
Colour - Hyperbasophilic?
Inclusions or vacuoles?
Emperipolesis / cannibalism
-
Criteria of malignancy within the NUCELOLI are more important than those of the NUCLEI, which in turn are more important than those of the CYTOPLASM.
